SHORT NEWS
More targeted therapy for multiple sclerosis
Researchers have created a reference database of a blood marker that can be used to measure the disease state of patients with multiple sclerosis. They hope this will open the way to more targeted and personalised therapies.

Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system that predominantly occurs in relapses. In recent decades, numerous new therapies have emerged that can reduce the number and severity of relapses and thus the deterioration of health. Nevertheless, there are patients for whom the chosen treatment is only insufficiently effective or can lead to serious side effects in the long term.
Researchers led by Jens Kuhle from the University Hospital and the University of Basel now report in the journal "Lancet Neurology" that they have validated a blood marker that provides information about the current disease activity and thus also about the probability of inflammatory relapses or a worsening of the health condition in the next year. The marker thus helps to assess whether someone is responding well or poorly to a therapy - or whether it should be adjusted if necessary.
Corrected for age and weight
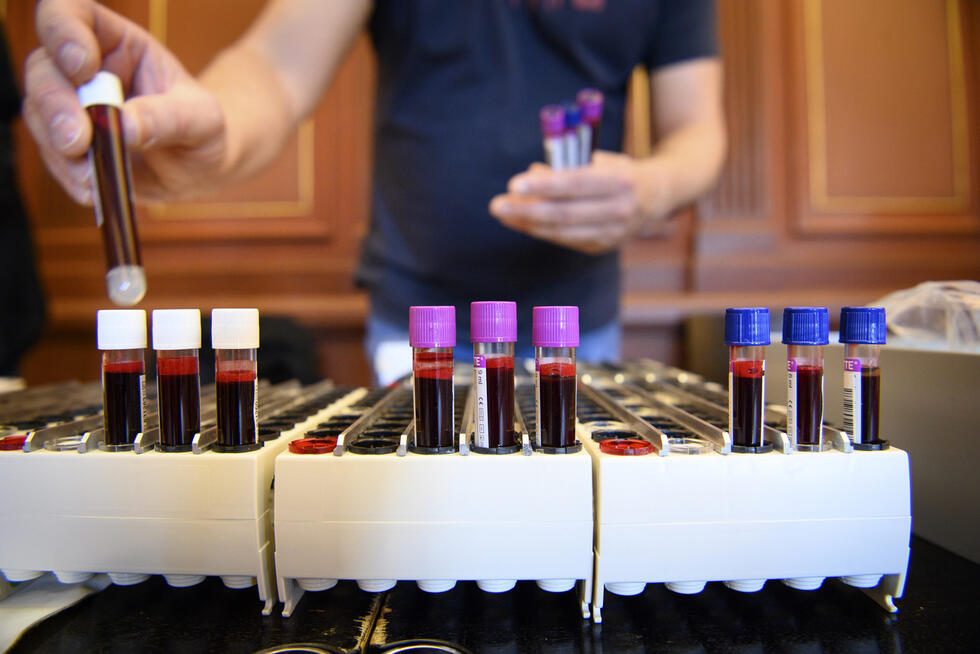
The blood marker is the neurofilament light chain protein (NfL). It has long been considered a marker that indicates that neurodegenerative processes are taking place and that damage to the nervous system is progressing. However, because there were previously no reference values that took into account the age-dependent increase and the influence of body weight, it was difficult to assess the diagnostic benefit of this biomarker in individual cases, the researchers write in their paper.
Now they have closed this gap: They created a reference database in order to be able to draw reliable conclusions from the NfL concentrations. More than 20,000 blood samples from over 10,000 people with MS and control subjects were included in the database.